- Track only production environment vulnerabilities and are willing to ignore the risk that vulnerabilities may pose in non-production environments in order to save time and resources.
- Track only top-level packages, and may not have visibility into the complete list of transitive dependencies those packages are pulling in.
- Have visibility on a per business unit basis, and have no automated way to determine organization-wide risk posed by a vulnerability, making prioritization and triage more difficult.
These kinds of blind spots generate unnecessary risk that can only be reduced by improving open source visibility, which requires:
- Implementing robust tracking and reporting systems.
- improving communication and information sharing across teams.
- Utilizing automated tools that can support the breadth (i.e., across multiple applications, deployment environments and business units), as well as depth (i.e., the entire dependency tree down the lowest level transitive dependency) necessary to assist in vulnerability detection and remediation.
But implementing these kinds of tools and practices can be highly resource and time consuming. Add to this the fact that vulnerability remediation is just one of many tasks required to secure your software supply chain, and it becomes imperative to find a comprehensive tool that can help minimize both implementation effort and vulnerability risk.
The Challenges of Open Source Observability
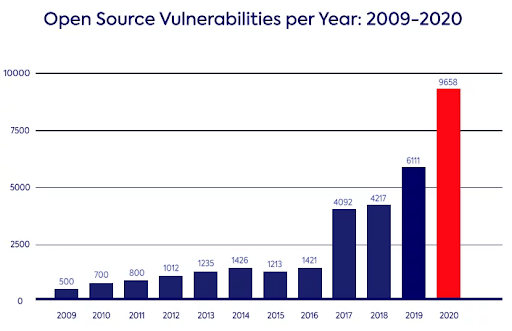
The discovery of open source vulnerabilities has skyrocketed in the past few years:
Source: mend.io
This is largely a function of three factors:
- More organizations are using more open source, and reporting the defects they find.
- Hackers are increasingly targeting open source packages due to the economies of scale: a single compromised package incorporated into a popular software application can allow them to potentially hack thousands of customers.
- 80% of codebasesare never updated for fear of breaking the build, which leads to applications riddled with open source vulnerabilities.
All of which translates into more risk and an ever-increasing load on security teams and the developers that inevitably need to address the vulnerabilities found.
Vulnerability Risk of Silos
On a project to project basis, though, the presence of business and/or software development silos can introduce a number of exacerbating factors beyond just a lack of communication and coordination:
- Each project may have different ways to obtain the open source resources they require, including risky processes like downloading prebuilt, unsigned packages or source code from public repositories.
- For example, coders that work in sandboxes (such as Data Scientists) often work around repositories of secure components, and pull unsigned packages directly from public repositories
- Even when a project builds all the open source artifacts they require from source code, they may do so on an unsecured developer desktop rather than a hardened build service.
- Finally, are the artifacts deployed from a central repository that tracks vulnerabilities and recommends updates? Or are they deployed from a prebuilt distribution that quickly becomes out of date?
The impact of security silos both within a business unit and across the extended enterprise impacts risk assessment, prioritization, and remediation. Multiple disparate tools and processes will lead to inconsistent and incomplete views of vulnerabilities, making it difficult to accurately assess risk, prioritize efforts, and remediate issues.
ActiveState Eliminates Open Source Vulnerability Silos
Open source observability is key to breaking down security silos. For ActiveState, observability means:
- Understanding all of the dependencies in use in your organization, including all transitive dependencies, shared libraries and OS-native binaries.
- Understanding where each set of dependencies is deployed across the extended enterprise.
The result is a comprehensive view of vulnerabilities across the entire enterprise, enabling more effective risk assessment and remediation efforts.
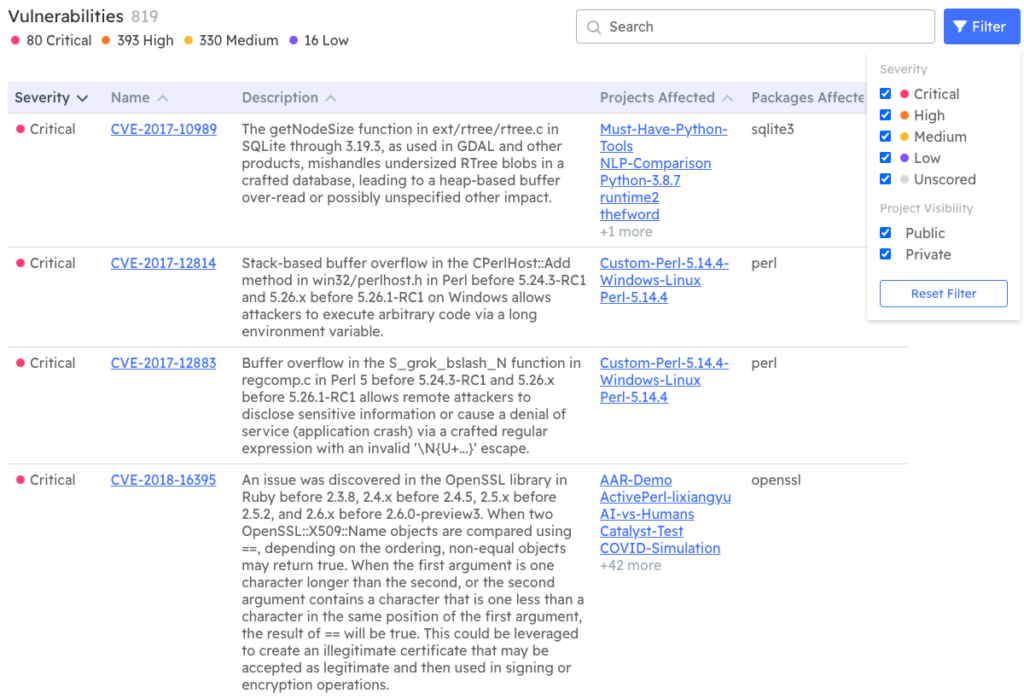
It also allows security teams to regain control over proliferating projects and the open source dependencies they require by providing a single, central view of all the Python, Perl, Ruby and Tcl projects deployed in every environment across the extended enterprise:
- Visualize the security status of every project.
- Filter by severity.
- Search for specific CVEs.
- At-a-glance view of number of affected projects, facilitating triage.
- Comprehensive list of affected dependencies, including all transitive dependencies.
Uniquely, security teams can Immediately update projects with newer (fixed) versions of vulnerable packages, automatically rebuild the runtime environment ready for testing, and thereby decrease Mean Time To Remediation (MTTR).
Next steps:
To start securely integrating open source into your build process and creating reproducible developer environments, get started with a free ActiveState account now.