Download ActiveState Python to get started or contact us to learn more about using ActiveState Python in your organization.
Most Python packages are now designed to be compatible with Python’s pip package manager. But if you have a package that is not compatible with pip, you’ll need manually install Python packages. Here’s how.
Python Installation Checklist
Before installing any package, you should always ensure that a Python installation containing the necessary files needed for installing packages is in place by following the Installation Requirements.
Packages That Cannot be Installed with Pip
Preliminary Steps to take:
- Download the package and extract it into a local directory.
- If the package includes its own set of installation instructions, they should be followed. Otherwise, the most common method for manually installing a package is to implement
setup.py.
Installing Python Packages with Setup.py
To install a package that includes a setup.py file, open a command or terminal window and:
- cd into the root directory where
setup.pyis located - Enter:
python setup.py install
Setup.py Build Environment
Packages installed with setup.py have build requirements that developers must adhere to. However, some requirements are optional.
Examples
- Ensure that an up-to-date version of setuptools is installed:
python -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
- Include
install_requireskeyword arguments in setup.py. install_requires is a setuptools setup.py keyword used to specify minimum package requirements. For example:
install_requires=['<packagename>'], # Optional keyword
Complete package build requirements for a setup.py based installation are outlined by PyPA (Python Packaging Authority) in ‘Sample Project’.
Sample Project
Sample Project is a template package with a setup.py file for manual installation of a package. The file is annotated with comments for customizing the script, and for the overall package build environment. [https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject ]
Sample Project is based on the setuptools package: “A setuptools based setup module.” https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject/blob/master/setup.py ]setup.py is the build script for packages built with setuptools.
Setup.py Example (Non-Annotated)
import setuptools
with open("README.md", "r") as fh:
long_description = fh.read()
setuptools.setup(
name="<template-package-username>", # Replace with your username
version="1.0.0",
author="<authorname>",
author_email="<authorname@templatepackage.com>",
description="<Template Setup.py package>",
long_description=long_description,
long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
url="<https://github.com/authorname/templatepackage>",
packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
classifiers=[
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
python_requires='>=3.6',
)How ActiveState Can Help
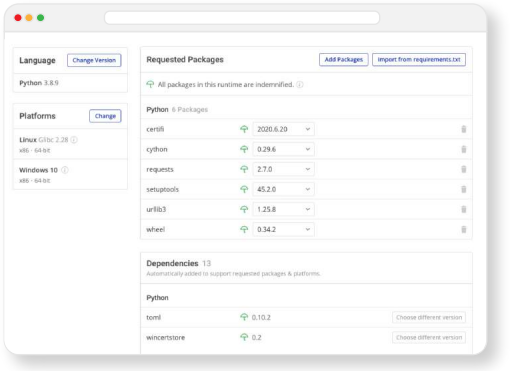
ActiveState provides a unified cross-platform toolchain for modern Python package management. It can replace the complex and hard-to-maintain in-house solutions built from multiple package managers, environment management tools and other solutions.
By adopting the ActiveState Platform, developers can:
- Automated building of packages from source, including link C libraries without the need for a local build environment.
- Automated resolution of dependencies (or suggestions on how to manually resolve conflicts), ensuring that your environment always contains a set of known good dependencies that work together.
- Central management of a single source of truth for your environment that can be deployed with a single command to all development and CI/CD environments, ensuring consistent reproducibility.
- Automated installation of virtual Python environments on Windows or Linux without requiring prior setup.
- The ability to find, fix and automatically rebuild vulnerable environments, thereby enhancing security and dramatically reducing time and effort involved in resolving CVEs.
- Visually seeing which versions of which packages are approved for use, thereby taking the guesswork out of development.
Those that prefer to work from the command line can leverage the ActiveState Platform’s CLI, the State Tool, which acts as a universal package manager for Python, and provides access to most of the features offered by the Platform.
Modern Python Package Management
ActiveState provides a unified cross-platform toolchain for modern Python package management. It can replace the complex and hard-to-maintain in-house solutions built from multiple package managers, environment management tools and other solutions.
By adopting the ActiveState Platform, developers can:
- Increase the security of Python environments
- Improve the transparency of your open source supply chain
- Dramatically reduce package and environment management overhead
- Eliminate dependency hell
- Reduce “works on my machine” issues
Ultimately, developers that are willing to adopt the ActiveState Platform will spend less time wrestling with tooling and more time focused on doing what they do best: coding.
To try the ActiveState Platform for yourself, sign-up for a free account.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I manually install Python packages?
If necessary, you can manually install packages in Python. Some packages have special installation requirements. Other packages can be installed manually with setup.py. To manually install packages in Python with setup.py, do the following:
- Download the package and extract it into a local directory.
- Navigate to the directory in which you’ve extracted the package.
- If the package includes its own set of installation instructions, they should be followed. Otherwise, use setup.py by running the following command:
python setup.py install
You may still need the setuptools library to complete the package build requirements.
See how to install pip on Windows.
How do I install Python packages without setup.py?
pip install <packagename>Where packagename is the name of the package to be uninstalled.
Learn more about installing Python packages with pip.
How do I manually install pip?
Installing a Python distribution like ActivePython, which includes pip, or manually installing pip with get-pip.py: Download get-pip.py. Navigate to the directory where you installed get-pip.py. Run the following command:
python get-pip.pyLearn more about installing pip.
How do I install Python IDLE packages?
pip install <packagename>Where packagename is the name of the package to be installed.
How to install Python packages using pip.